Steven Meyer, M.Sc.
Contact
Telephone
(+49)231 755-2352
Address
Department of Biochemical and Chemical Engineering
Laboratory of Solids Process Engineering
Room G3-4.23
Emil-Figge-Str. 68
44227 Dortmund
Contents
Abstract
A large number of drug candidates for future use exhibit low water solubility. This makes the production of highly effective oral dosage forms challenging. In amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs), the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is molecularly dispersed in a polymer matrix, which ultimately improves the drug release behavior. Hot melt extrusion (HME) is a key technology for the production of ASDs. However, the dissolution of the API into the polymer matrix is highly dependent on the selected process conditions.
Description
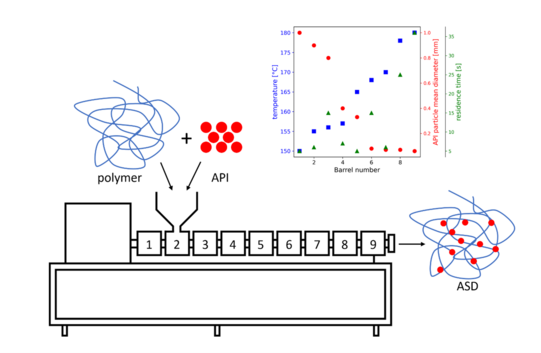
The dissolution process of the API into the polymer matrix mainly depends on dependent critical process parameters (DCPP), such as temperature, residence time and particle size. However, in contrast to the critical process parameters (CPP), such as screw speed, throughput and screw configuration, these are not directly adjustable during the extrusion process. For this reason, models are developed which allow a prediction of the DCPPs as a function of the CPPs. An example of these experiments is the investigation of the particle size as a function of the residence time when using different screw elements. The process analytical technology of the extruder is also extended for these investigations.
Next, the dissolution process is modeled. For this, the degree to which the API dissolves in the polymer at different DCPPs is investigated. Combining these models allows a prediction about whether the active ingredient dissolves completely over the length of the extrusion process. This also makes it possible to find optimal process conditions with minimal experimental effort. In addition, the degradation of the polymer/API during the process is modeled in order to prevent this in the process by selecting suitable process restrictions.
In the final step, the models are implemented in a software package that enables the optimal selection of process conditions.