Yunwen Liu
Contact
Telephone
(+49)231 755-2329
Address
Department of Biochemical and Chemical Engineering
Laboratory of Solids Process Engineering
Room G3-4.16
Emil-Figge-Str. 68
44227 Dortmund

Contents
Abstract
This research aims to address current demands regarding the sustainability and recyclability of product packaging. The focus is on the use of a twin-screw extruder to produce cellulose-based biodegradable packaging materials from plant fibres. The project includes extrusion process design, plant cellulose analysis and fibre property technology to optimize the product performance. The final assessment evaluates the overall extrusion manufacturing process and energy consumption, providing an environmentally friendly packaging solution while highlighting future development potential
Description
Over the past few decades, global plastic production has grown exponentially, with 40% of plastics used in packaging materials [1]. However, compared to plastic production, the world is unprepared to deal with plastic waste, leading to serious environmental problems. Plant fibres, as biodegradable materials, could significantly reduce the environmental pollution caused by improper disposal of plastic packaging if widely developed and applied in packaging production, offering significant growth prospects. However, the three-dimensional shaping of cellulose-based materials remains an area of research. The aim of this project is therefore to investigate the utilization of extrusion processes to prepare plant fibre pulps that are suited for a subsequent three-dimensional moulding of cellulose composite packaging.
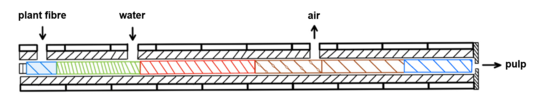
In papermaking processes, the pulp production requires the application of dispersion and distribution of the fibre material. This is conventionally performed discontinuously in large pulpers, leading to drawbacks such as longer processing times and wide distributions of material properties. The utilization of twin-screw extrusion ensures a continuous application of dispersion and distribution forces [2,3] and therefore overcomes the problems associated with discontinuous processes. Considering different screw configurations and adjusting specific process parameters, an optimization of the pulp production is performed.
Understanding how variations in cellulose structure under different conditions affect product performance is critical to the success of the project. Therefore, the project includes not only the design and optimization of extrusion processes, but also the analysis of the interaction between plant cellulose and water, as well as techniques for analysing fibre properties. The final stage of the project will involve the evaluation of the extruder manufacturing process and a detailed energy consumption analysis to ensure both product quality and production efficiency.
This project is made possible by the funding of the AiF and
is a cooperation of the Laboratory of Solids Process Engineering (TU Dortmund), the Department of Machine Elements (TU Dortmund), the Institute of Natural Materials Technology (TU Dresden) and
the Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging (IVV)
References
- Plastics Europe: Plastics - the Facts 2021: An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. 20.05.2022
- Reitz, E.; Podhaisky, H.; Ely, D. R.; Thommes; M.: Residence time modeling of hot melt extrusion processes. In: European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics (2013), Nr. 85, S. 1200–120
- Thommes, M.; Kleinebudde, P.: Properties of pellets manufactured by wet
extrusion/spheronization process using kappa-carrageenan, Effect of process parameters. In: AAPS Pharm SciTech (2007), Nr. 8, E95
Curriculum Vitae
| Since 2023 | PhD at the Laboratory of Solids Process Engineering, TU Dortmund |
| 2021 - 2023 | M. Sc. Pharmaceutical Engineering, Anhalt University |
| 2019 - 2021 | B.Sc. Pharmaceutical Engineering, Anhalt University |
| 2017 - 2021 | B. Sc. Bio Engineering, Henan University |
| Born | January 30th, Henan (China) |


